Invasive Species Ontario - Threats and Advanced Management
Invasive Species Ontario pose serious threats to native ecosystems. Discover advanced tech solutions transforming detection and control across landscapes.
Written by Maryam
Reviewed by Boshra

The ecological and economic integrity of Ontario's landscapes faces a persistent threat from non-native flora. Managing this issue requires a sophisticated understanding of the threats and the advanced tools available for intervention. This article moves beyond conventional methods to explore how cutting-edge technologies, led by innovators like Saiwa, are providing a powerful, data-driven response to this environmental challenge.
Common Invasive Species in Ontario
To grasp the full scope of this challenge, it is essential to identify the key species causing widespread disruption. The following list details some of the most problematic invaders, each with its own unique method of damaging local ecosystems.
Giant Hogweed
A public health hazard, this plant’s sap contains phototoxic chemicals that cause severe burns and blistering when exposed to sunlight. Its towering presence allows it to outcompete native vegetation for light.
Wild Parsnip
Similar to Giant Hogweed, Wild Parsnip's sap can cause painful burns and rashes. It spreads rapidly along roadsides and in open fields, displacing native wildflowers and forage plants.
Goutweed
Often sold as an ornamental ground cover, this species forms dense, suffocating mats that choke out all other plants, creating sterile monocultures in forest understories and gardens.
Garlic Mustard
This biennial herb releases chemicals into the soil that inhibit the growth of other plants, including the fungi that many native trees depend on. Its rapid spread dramatically alters forest floor composition.
Dog Strangling Vine
This aggressive vine blankets entire areas, smothering native plants and small trees. It is also a significant threat to Monarch butterfly populations, as they mistakenly lay their eggs on it.
Flowering Rush
An aquatic invader, Flowering Rush forms dense stands in rivers and lakes, impeding water flow, interfering with recreational activities, and displacing native aquatic vegetation.
European Water Chestnut
This floating aquatic plant creates thick mats on the water's surface, blocking sunlight, reducing oxygen levels, and hindering boaters and swimmers.
Read Also : Taraxacum Officinale Control - Innovations in AI and Machine Learning

Threats of Invasive Species to Plants in Ontario
The presence of these species creates a cascade of negative effects that destabilize entire ecosystems. The threats posed by Invasive Species Ontario to native flora are multifaceted and severe, impacting environments in several critical ways.
Competition for Resources: Invaders aggressively consume essential resources like sunlight, water, and soil nutrients, leaving native species unable to thrive.
Soil Chemistry Alteration: Plants like Garlic Mustard release allelopathic chemicals, changing soil composition to create an environment hostile to native flora.
Threat to Biodiversity: By outcompeting and eliminating native plants, these invaders create fragile monocultures, reducing the variety of life that the ecosystem can support.
Read Also : Water Soldier Control - Modern Solutions for a Growing Threat
Advanced Methods of Invasive Species Control
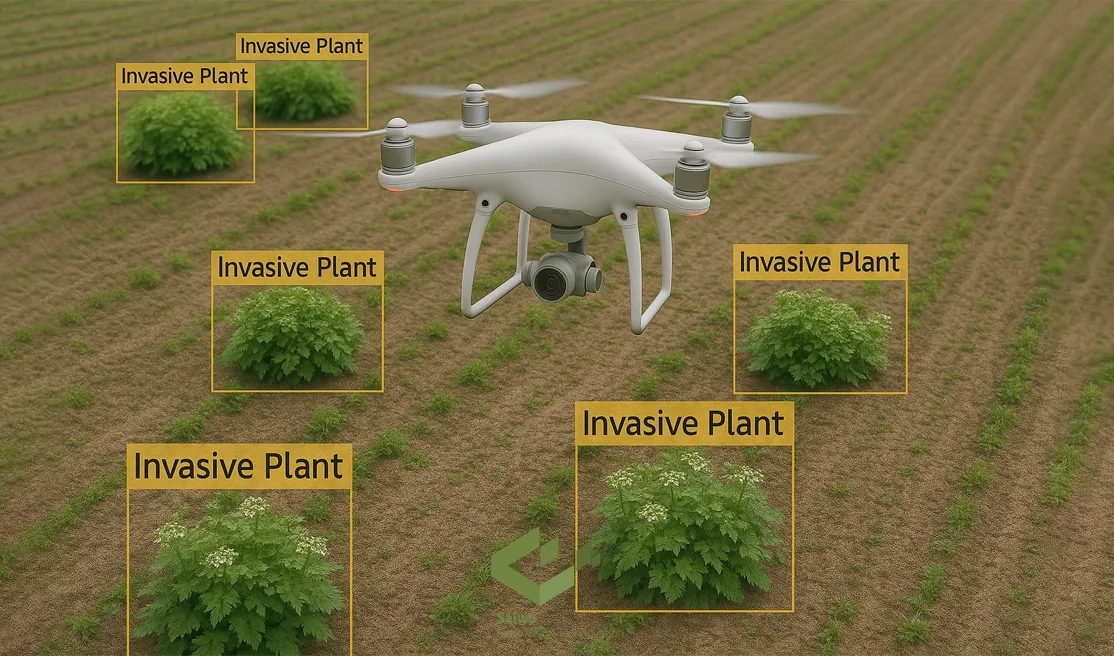
Fortunately, the fight against these invaders is evolving from manual labor to high-tech precision. Modern strategies leverage technology to provide a quantitative advantage, as detailed in the approaches below.
Read Also : Smart Strategies for Managing Goosefoot with AI-Driven Tools
Drones with AI-Based Image Detection
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras provide an invaluable aerial perspective. When coupled with advanced algorithms, this technology enables sophisticated Weed detection and mapping of infestation hotspots with unparalleled speed and accuracy.
Remote Sensing Monitoring
Satellite and aerial imagery allow for large-scale monitoring of vegetation changes over time, helping ecologists track the spread of invasive species and assess the effectiveness of control measures across vast landscapes.
Hyperspectral and Thermal Imaging
These advanced imaging techniques see beyond the visible spectrum. They can detect subtle signs of plant stress and differentiate between species based on their unique spectral signatures, enabling early and precise identification.
Robotics and Smart Precision Herbicide Systems
Automated ground robots can navigate fields and forests to apply herbicides directly to target invasive plants, drastically reducing chemical usage and minimizing collateral damage to surrounding native vegetation.
Read Also : Chamomile Weed Management - Crop Protection Through Smart Technologies
Invasive Species Control with Sairone’s Smart Technology
Effectively managing invasive species Ontario requires a tool that bridges the gap between data collection and actionable strategy. Sairone, by Saiwa, achieves this by automating the analysis of drone imagery to identify and map invasive species with scientific precision.
This technology empowers farmers, ecologists, and land managers to move from reactive cleanups to proactive, targeted interventions, saving immense time and resources. Sairone’s platform is also a pivotal tool for AI in wildlife conservation, ensuring that habitat restoration efforts are based on accurate, real-time data.
Read Also : Revolutionizing Amaranthus Palmeri Control with AI and Automation

Conclusion
The challenge posed by invasive species is significant, but the technological horizon is promising. Advanced methods are transforming our ability to manage these threats effectively. The core principle remains early and accurate detection, a capability that Sairone’s smart technology elevates to a new level, making proactive and precise ecosystem management a tangible reality.
Note: Some visuals on this blog post were generated using AI tools.
Comments
No comments yet!
Table of Contents
No headings were found on this page.
