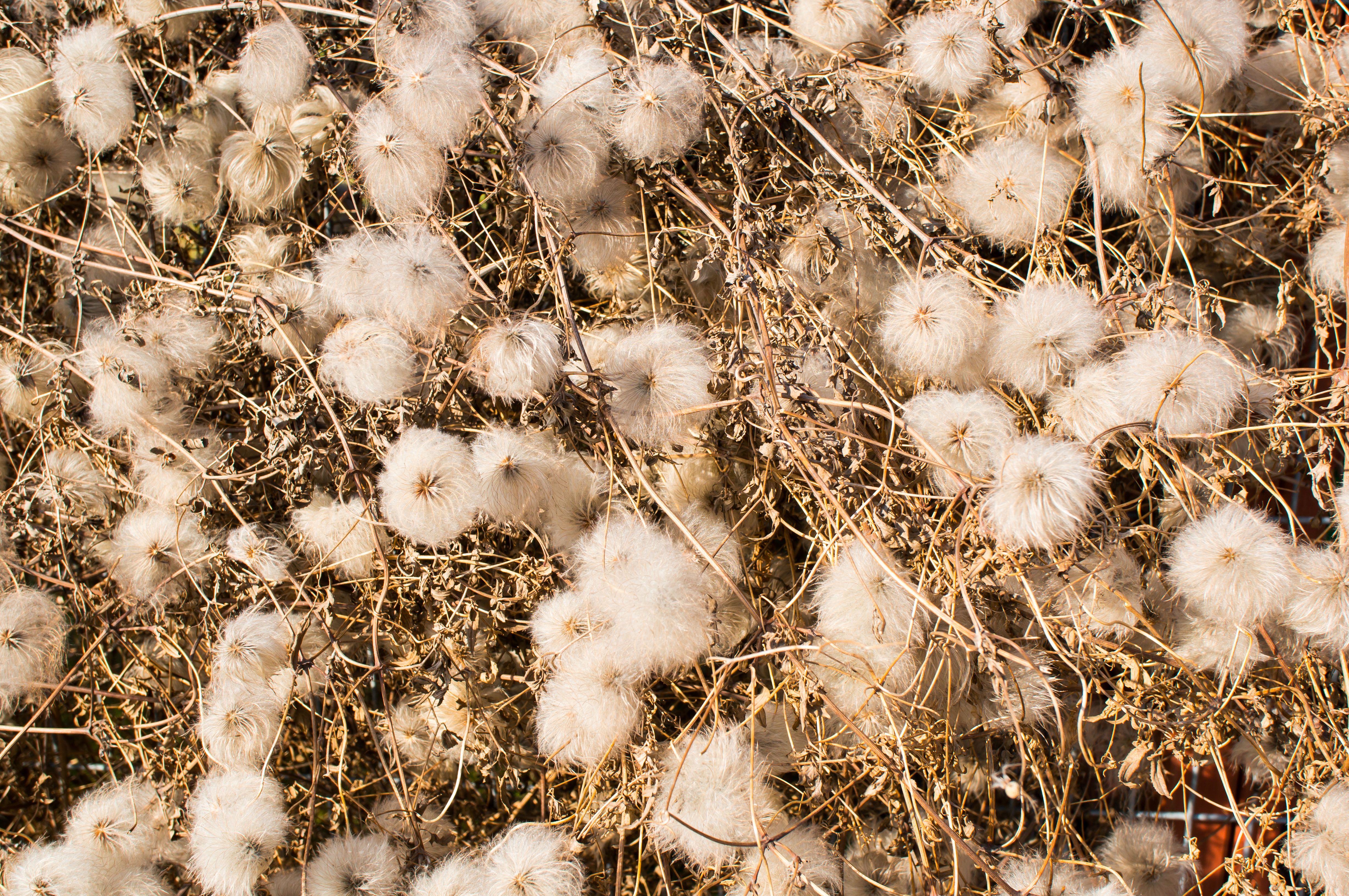
Thistle
Controlling Thistle in any crops
No matter which variant, control them.
Cirsium muticum
Cirsium muticum is a biennial plant that reaches a height of 180 centimetres (71 in).
Cirsium arvense
Cirsium arvense is a C3 carbon fixation plant. The C3 plants originated during Mesozoic and Paleozoic eras
Cirsium palustre
Cirsium palustre is a tall thistle which reaches up to 2 metres (7 ft) in height.
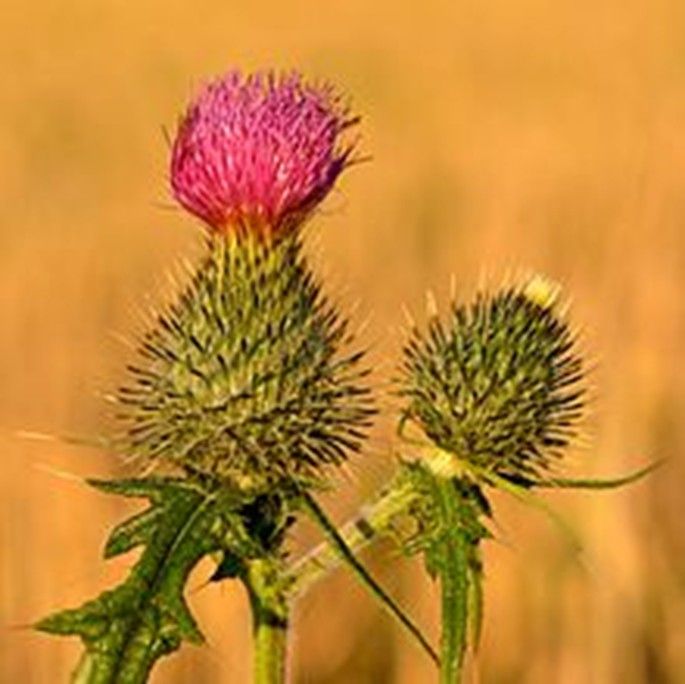
Cirsium vulgare
The plant can reach a height of1.5 m (but sometimes it can even exceed 1.5 m)2 m up to3 m) is normally high on50-70 cm.
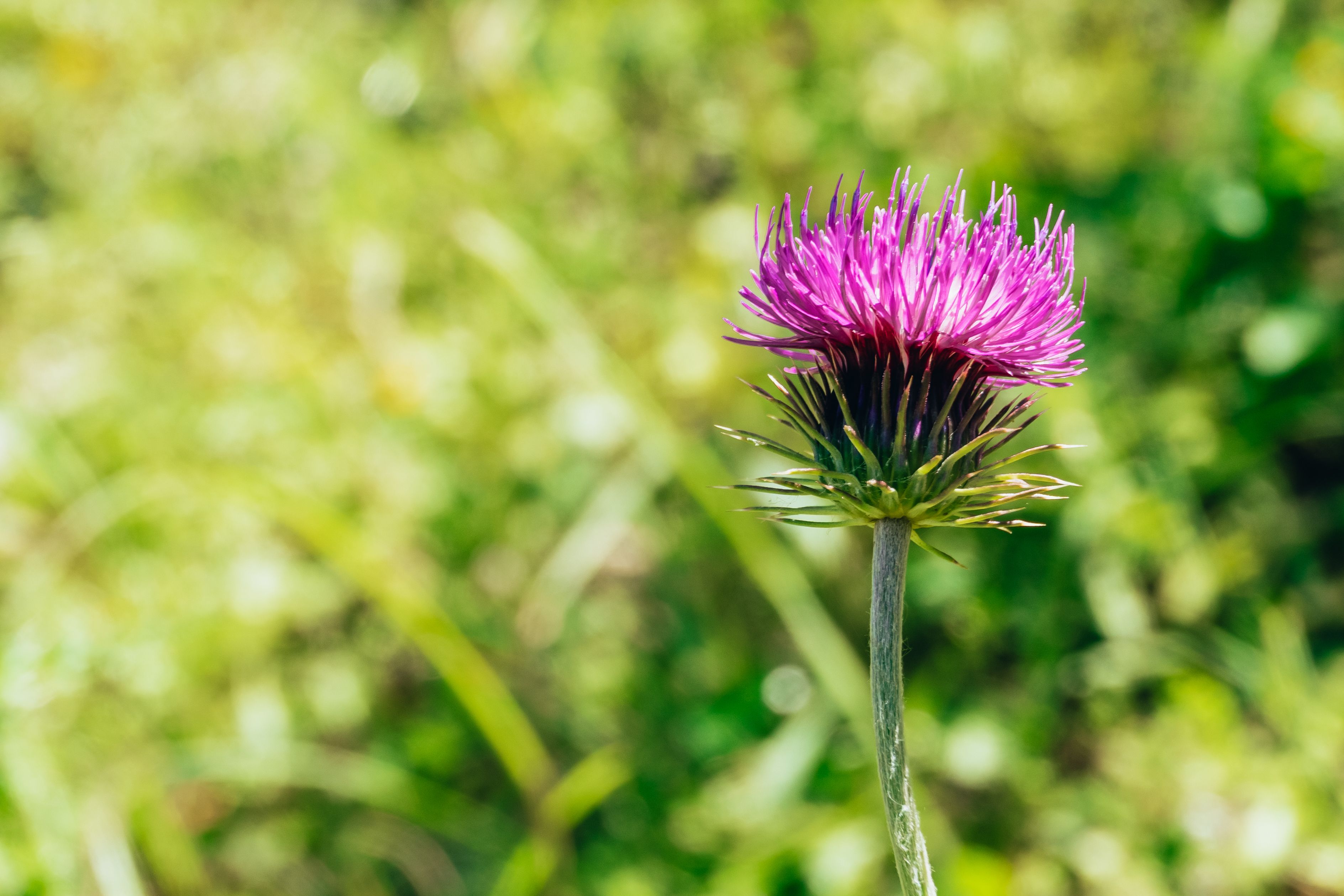
Thistle is a common name for a group of spiny, invasive weeds from the Cirsium, Carduus, and Onopordum genera. These weeds are prevalent across Europe, North America, Australia, and parts of Asia, thriving in disturbed soils, rangelands, pastures, and roadsides. They are especially problematic in temperate and semi-arid regions, where they can spread rapidly and form dense, impenetrable patches that are difficult to manage and reduce land usability.
Thistles are identified by their spiny, lobed leaves and tall, upright stems that can reach over 1.5 meters. They typically produce purple, pink, or occasionally white flower heads that resemble pompoms and bloom in summer. One of the most notorious species is Cirsium arvense (Canada thistle), a perennial with creeping roots, while Carduus nutans (musk thistle) and Onopordum acanthium (Scotch thistle) are biennial species with large, solitary flower heads. These variants differ in growth habit, height, and seed production, but all share the characteristic spiny foliage and strong reproductive capacity through seeds or underground rhizomes.
Thistles pose serious problems for forage crops, rangelands, and cereal production, especially wheat and barley. They reduce pasture quality, hinder livestock movement and grazing, and compete aggressively with crops for water and nutrients. Control is challenging due to their extensive root systems and seed banks. Successful management requires an integrated approach, including targeted herbicide applications, mechanical removal before flowering, and maintaining competitive vegetation to prevent re-establishment. Biological control agents, such as specific insects, have also been introduced in some regions to curb their spread.
Example of processing and outputs
A variety of outputs are available
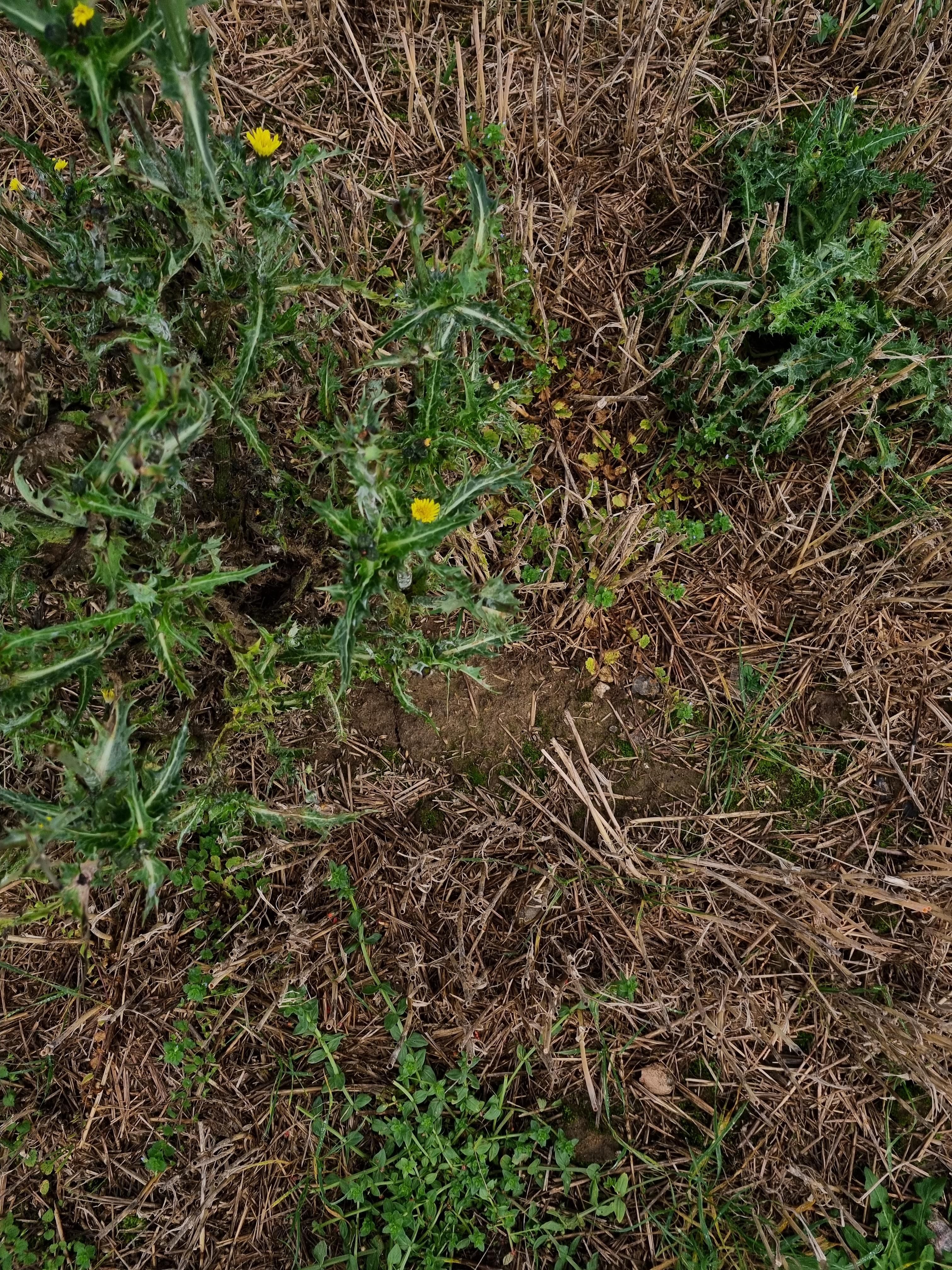
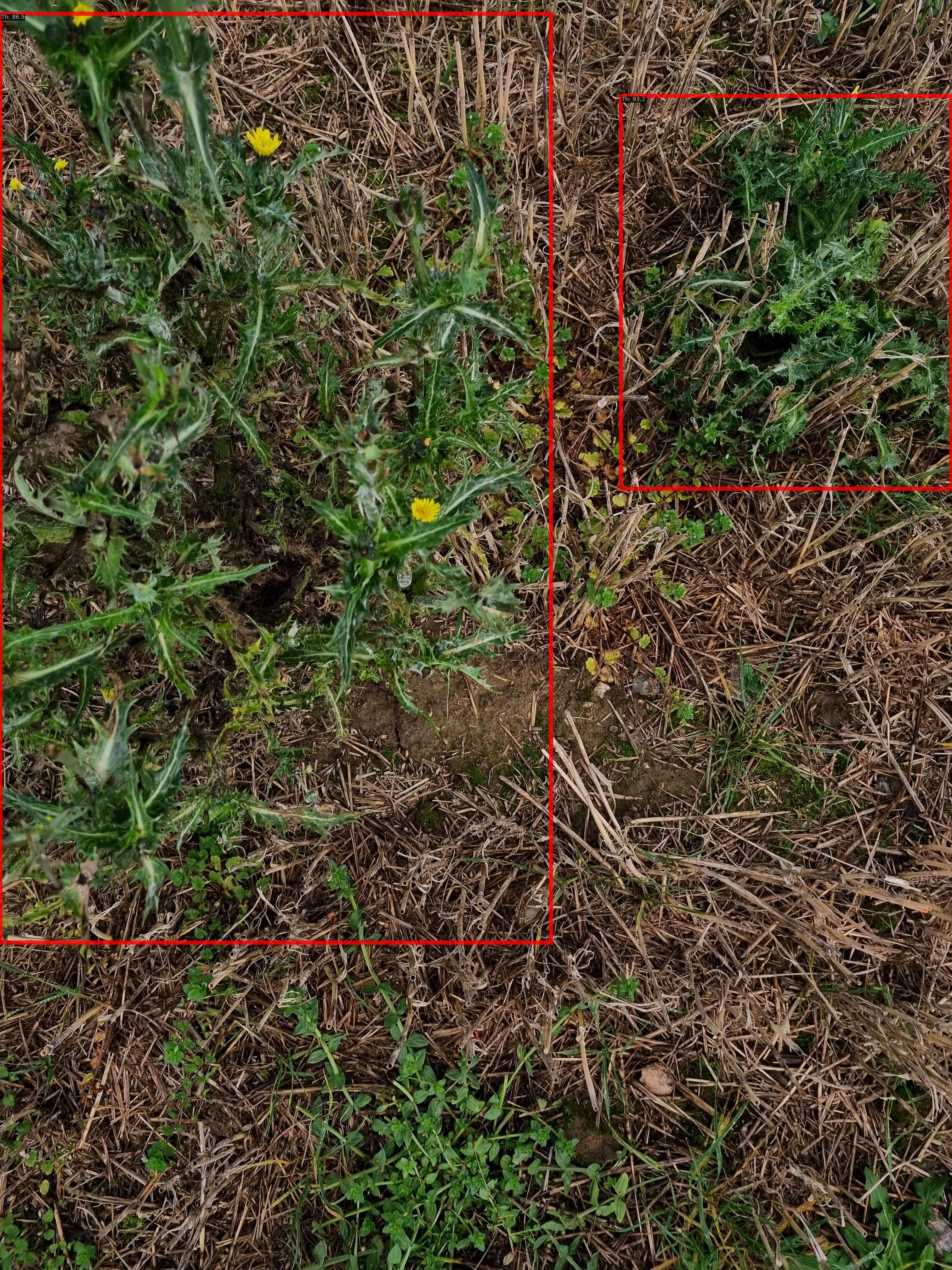


We employ a cutting-edge, real-time object detection model to identify Thistle and other invasive species efficiently. This model is designed to balance high-speed inference with accuracy, making it ideal for real-time applications.
Ready to elevate your Images/Videos?
How it works?
Easy to use online cloud-based web service
Upload Images/videos
Aerial videos/images in various formats Orthophoto/TIFF images RGB, multispectral, thermal Surveillance (CCTV) cameras Agricultural machinery camera
Processing
in second
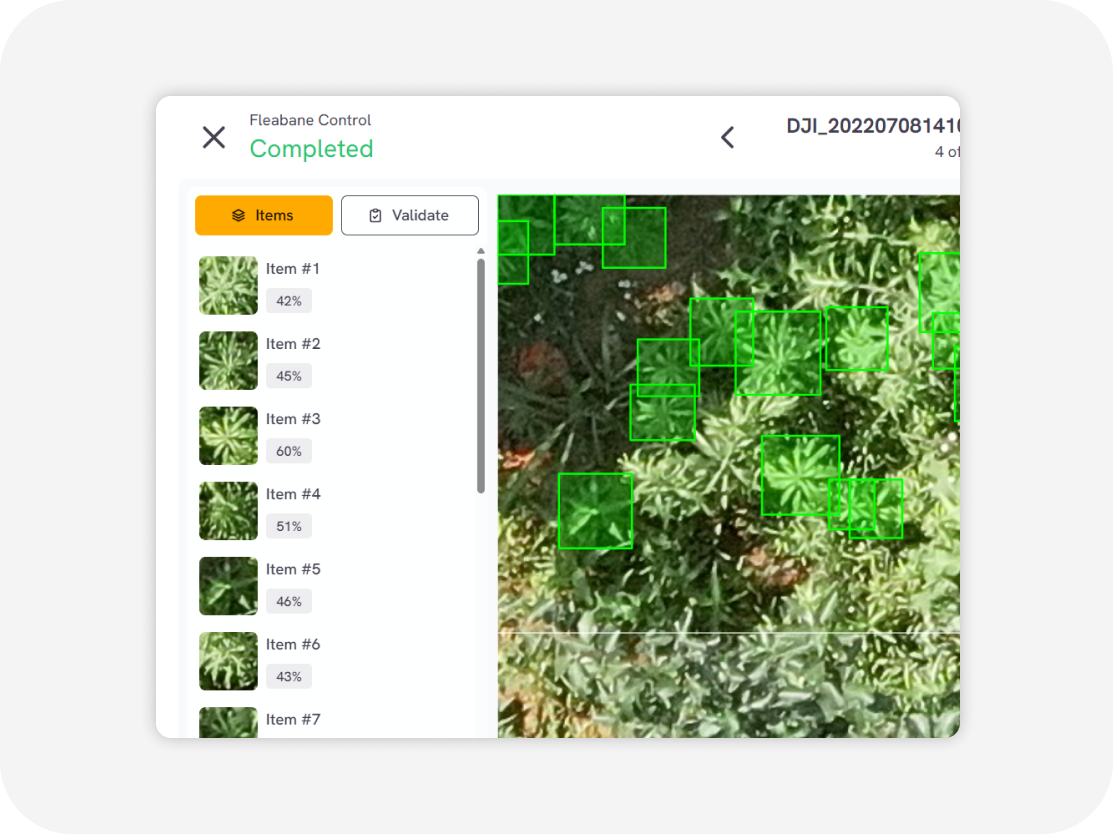
Download output
Weed distribution map with GIS data Weed clustering map with GIS data (GeoJSON, Shapefile, KML, CSV)
Thistle control in various crops
Flexible Service Delivery
API Integration
Seamlessly connect Sairone’s advanced AI services to your existing systems through modular, easy-to-use APIs.
Fully White-Labeled Solutions
Get a tailor-made version of Sairone—branded, customized, and built specifically for your unique business needs.
Online Web Application
Use our powerful online platform with scalable cloud processing and budget-friendly
Try it for free now
Contact us if you have any questions

















