Exploring the Future with AI-Based Farm Equipment
Discover how AI-powered farm equipment is revolutionizing agriculture with automation, precision farming, and increased efficiency.
Written by Amirhossein
Reviewed by Boshra

Agriculture is entering a new phase where traditional machinery is being reimagined through artificial intelligence. As farms face rising labor shortages and more complex production demands, manual equipment often struggles to keep pace and maintain consistent results. AI-powered farm machinery helps solve these limitations by learning from field conditions, adapting to real-time data, and performing tasks with far greater precision than conventional tools.
This article explores how AI is reshaping modern equipment, from autonomous tractors and robots to drones, greenhouse systems, and advanced analytics, giving you a clear understanding of their benefits, applications, and future potential.
Read Also: Practical Application & Future of AI in Agriculture
Autonomous Tractors and Farm Robots
Driverless tractors with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) are already deployed in farms, paving the way for complete autonomy. These "smart" machines leverage a combination of GPS systems, LiDAR sensors, computer vision cameras, AI algorithms, and more to automate a variety of field tasks.
Tractor Auto-Steering and Navigation Technologies
Tractor auto-steering and navigation using GPS ensures accurate parallel passes through crop fields with centimeter-level precision. Machine vision detects obstacles like humans, animals, irrigation lines, etc. to enable safe autonomous driving and path planning. Reinforcement learning algorithms analyze data from hundreds of acres to determine ideal seed/fertilizer dispensing, soil tilling, and crop picking patterns. In essence, AI-based farm equipment makes tractors "aware" and intelligent.
The key benefits of AI-based farm equipment include reduced driver fatigue, lower fuel usage, minimized soil compaction, higher field precision, and accident avoidance. Farmers are freed to focus on higher-level crop management Crop Disease Detection and strategy tasks. Startups like Bear Flag Robotics offer AI-powered autonomous tractor hardware and software solutions.
AI in Specialized Agriculture Robots
Specialized agriculture robots are automating repetitive field tasks that are dangerous, labor-intensive, or require precision. Robotic milking systems use computer vision to attach milker cups onto cow udders while monitoring hygiene. Weeding robots rely on deep learning to identify unwanted plants and selectively spray them. Strawberry-picking robots analyze fruit ripeness and quality data to harvest at peak conditions.
Overall, these emerging technologies provide farm owners with unprecedented monitoring, analytics, and automation capabilities. They enable sustainable food production using less labor, chemicals, and natural resources.
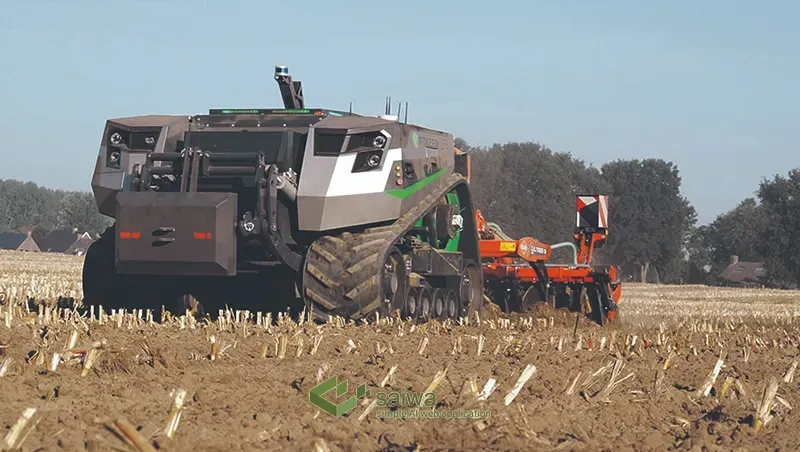

Applications of AI-based Farm Equipment
AI is being embedded into a wide array of farming systems and equipment beyond autonomous vehicles:
Aerial Crop Surveillance Drones
Specialized UAVs equipped with multispectral and infrared imaging can detect everything from pest infestations to water stress in crops when integrated with deep learning analytics. Soil and field analysis provides precise prescription maps for targeted interventions.
Read More: AI-Based Drone Operation| AI in Drones use cases
AI-Powered Greenhouses
In AI-powered greenhouses, sensor networks combined with computer vision continuously track climate parameters, growth, irrigation requirements, energy consumption, and more. AI platforms integrate this data to autonomously control temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, lighting, and more based on crop needs.
Read Also: An Over View Applications of Computer Vision in Agriculture
Livestock Health Monitoring
Smart collars, leg bands, and ear tags collect vast volumes of livestock data including temperature, motion, feeding, milk output, and more. AI algorithms recognize patterns in the dataset to estimate health status and predict lameness, estrus, calving, and other events proactively. This improves animal welfare and farm productivity.
In essence, AI-based farm equipment tech maximizes the economic and environmental sustainability of agriculture by optimizing crop yields per acre while minimizing wastage, manual labor, and resource inputs.
AI for Agricultural Data Analytics
Precision agriculture leverages machine learning, computer vision, and predictive modeling capabilities to extract actionable insights from the ocean of data generated by smart farming infrastructure:
Crop Phenotyping
Advanced image analytics enable accurate high-throughput screening and modeling of plant traits, growth stage, nutritional status, biotic/abiotic stresses, and other attributes across thousands of plants. This helps optimize breeding programs and gene editing.
Predictive Maintenance
Sensor data from farm implements is analyzed using techniques like anomaly detection and failure mode effects analysis (FMEA) to anticipate equipment failures. Proactive repairs and part replacement avoid costly breakdowns.
Farm Management Analytics
Machine learning models derive optimal strategies for resource allocation, production planning, irrigation planning, equipment routes, hiring, input procurement, etc. based on thousands of variables. Farmers gain higher ROI from data-driven decision-making.
Supply Chain Optimization
Sophisticated simulations combine supply-demand forecasts, real-time logistics monitoring, quality tracking, and more to minimize wastage, ensure traceability, and maximize profits across agricultural supply chains.
By converting big data into valuable business insights, AI is enabling a transition to evidence-based farming practices for enhanced sustainability and resilience.
Read more: Agri Tech Companies at the Forefront of Agricultural Evolution
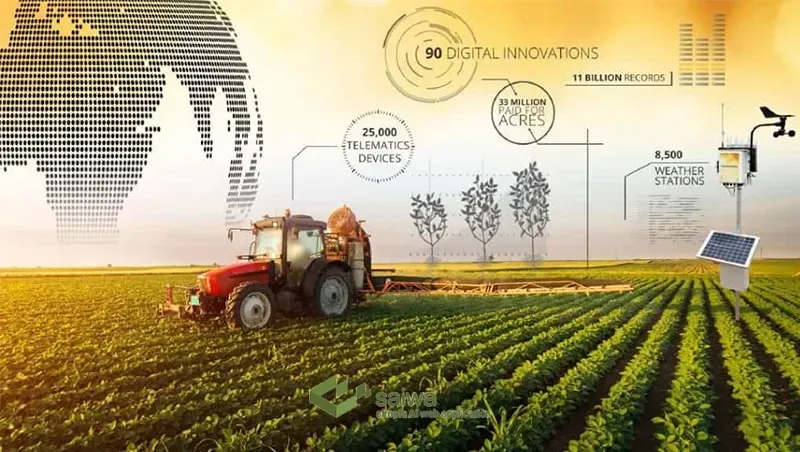
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing AI-based Farm Equipment
Despite the immense potential, significant adoption hurdles exist for AI-driven agriculture technologies:
Cost and Accessibility of AI-based Technologies: The high capital expenditure required for autonomous tractors, robotics, drone systems, data platforms, and more is often unaffordable for small farms. Innovative financing models can improve access. Our commitment in Saiwa, lies in pioneering innovative financing models, ensuring that even small farms can access and benefit from advanced AI technologies and AI-based equipment.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns: Farm data contains sensitive details like financial information, field locations, input utilization, etc. that raise security risks. Robust anonymization, encryption, and access control measures must be implemented to protect farmer interests.
Farmer Training Challenges: At Saiwa, we acknowledge the existing skills gap around operating new AI-powered tools and interpreting smart recommendations. To bridge this divide, we focus on comprehensive user training programs, and intuitive user interfaces, and even deploy conversational AI assistants such as Sairone with great analysis for farmers. Saiwa's commitment extends beyond technology; we are dedicated to empowering farmers with the knowledge and skills needed for seamless integration.
Addressing these challenges requires collective efforts from equipment manufacturers, agri-tech startups, government bodies, and farmer communities to drive education, supportive policies, and public-private collaborations for long-term technology adoption.
The Role of Edge Computing in AI Farm Equipment
While AI is revolutionizing agriculture with smart tractors, robots, and data-driven insights, there's a hidden hero behind the scenes: edge computing. This technology exists at the "edge" of the network, on the farm itself, where it processes data from AI farm equipment in real time. This is how edge computing empowers AI in agriculture:
Instantaneous Decisions
Traditional cloud computing can cause delays in data processing. Edge computing eliminates this lag, allowing AI farm equipment to make critical decisions instantly. Imagine a drone identifying a disease outbreak. With edge computing, the AI can analyze the data and trigger targeted pesticide applications right then, saving crops.
Reduced Reliance on Connectivity
Remote farms often have weak internet connections. Edge computing processes data locally, minimizing reliance on a strong internet connection for AI farm equipment to function. This ensures uninterrupted operation even in isolated areas.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
Sensitive farm data like crop health and soil conditions stay local with edge computing. This reduces the risk of breaches compared to sending everything to the cloud, offering greater security for AI farm equipment operations.
Faster Training and Experimentation
Edge computing allows for on-farm training of AI models specific to a farm's unique conditions. This enables AI farm equipment to adapt and learn faster, improving its effectiveness over time.
Conclusion
AI-enabled farm equipment is reshaping agriculture by bringing automation, precision, and deeper insight into daily operations. From autonomous tractors to intelligent greenhouses and advanced livestock monitoring, these systems enhance productivity while reducing labor pressure and resource waste. As the technology matures, the integration of robotics, sensors, and data analytics will continue driving farms toward more efficient and sustainable production.
From a professional perspective, the most meaningful shift is not the technology itself but the new decision-making power it gives to farmers. AI provides clarity where uncertainty once dominated, turning scattered data into practical guidance. The future of farming will belong to those who combine human experience with intelligent tools that elevate accuracy, safety, and long-term resilience. AI equipment is not replacing farmers, but empowering them to operate with confidence in an increasingly unpredictable agricultural landscape.
Note: Some visuals on this blog post were generated using AI tools.
References (4)
Comments
No comments yet!
Table of Contents
No headings were found on this page.
